How to Buy Brakes
A brake system causes your vehicle to stop or slow down when you press the brake pedal. The brake system may look very simple as the driver brings the speed of the vehicle down whenever required with a simple push of the pedal. However, internally, there is a complex system of various components working together to create a smooth braking experience. This buyer's guide explains the working of a brake system, its various inter-related components, along with the different possible causes of brake failure and their symptoms.
If you want to know more about BuyAutoParts.com's services and products, you can contact us on our toll-free number or e-mail. Our US-based sales and support teams are here to help you with your clarifications. We have professionals who are experienced in various automotive domains such as turbochargers, superchargers, steering and cooling systems. We will put the right professional in touch with you to help you with your queries.
Function of Brakes
The primary function of the brake system is to multiply the force applied on the brake pedal and use that force to decelerate or stop the wheels from rotating. For generating the required brake pressure, brake systems generally use a booster.
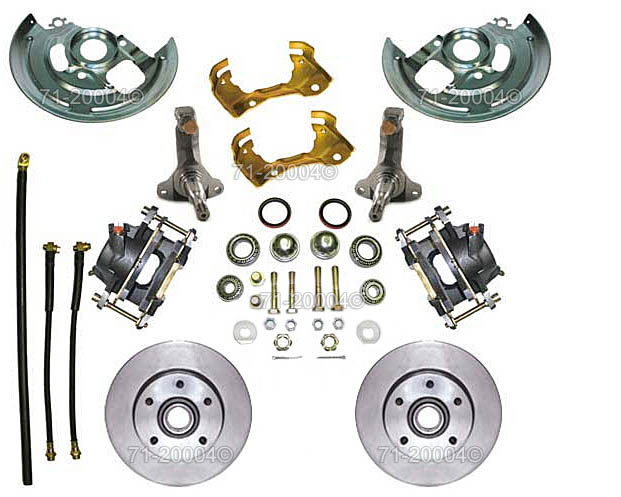

Kinds of Brake Systems Hydraulic Brake Systems Hydraulic brake systems, as the name implies, use hydraulic fluid for braking. Single-Circuit Hydraulic Brake Systems: In single-circuit brake systems, when the brake pedal is pressed, a piston in the master cylinder helps transfer the non-compressible brake fluid to the brake caliper/wheel cylinder. In drum brake systems, the brake caliper forces the brake pads to squeeze against the brake rotor. In disc brake systems, the wheel cylinder pushes the brake shoes towards the brake drum. Dual-Circuit Hydraulic Brake Systems: These brake systems control the braking with two circuits. When the brake pedal is pressed, the first circuit sends a signal to an on-board computer. The on-board computer then calculates the required brake pressure and instructs the second circuit which includes the master and slave cylinders to perform the requisite braking action. Dual-circuit hydraulic brake systems are efficient as they consider factors like the vehicle's speed to determine the ideal brake pressure. These brake systems are commonly employed in luxury automobiles. Brake-by-wire Systems Brake-by-wire systems are electronically-controlled braking systems. Brake-by-wire and dual-circuit hydraulic systems work similarly but are different in their design. Brake-by-wire systems use electronic wires to activate the brake system whereas the dual-circuit hydraulic systems use hydraulic fluid to activate the brake system. Parking Brakes Parking brakes are also known as hand brakes or emergency brakes. These brakes can be used to stop the vehicle when the standard brake system fails. Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) These systems are superior to standard braking systems. Anti-lock braking systems employ sensors to monitor the speeds of the car's wheels. The main advantage of anti-lock braking systems, as inferred from the name, is that they prevent the wheels from locking up in case of emergency stops, thereby preventing any serious damage to the driver and vehicle. Anti-lock braking systems are monitored by an on-board computer. If the computer senses any possibility of locking up, it vigorously pumps the brakes to prevent the vehicle from skidding. Air Brake Systems Air brake systems are generally found in heavy automobiles such as trucks, buses and trailers. These systems employ air instead of hydraulic fluid. Air-brake systems have a compressor that compresses air to provide the required brake pressure. |
Causes of Brake Failure
|
Symptoms of Failing Brakes
|
Maintenance
|
Why is the OEM number important for buying an auto part? Vehicle manufacturers designate the parts employed in their vehicles with an OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) number. Assigning an OEM number to parts helps identify them easily. OEM parts are usually produced by the manufacturers themselves or by a third party trusted by the manufacturers. There are two ways to get the right replacement part at BuyAutoParts.com: You can enter your car's year, make and model or your part's OEM number. The OEM number can usually be found on the part itself. If you are not sure of your part's OEM number, you can provide your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) to your dealership and get the right OEM number from your dealer. |
 |
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I replace the ABS speed sensor myself?
Before replacing your ABS sensor, check whether the ABS sensor is connected to the wheel hub via a connector or is integrated into the wheel hub assembly itself.
If the ABS sensor is inside the wheel hub, replacing will be a quite tricky process, as it will require removing the entire assembly and braking components. Otherwise, it is easy to do it yourself.
How to clean my brake system?
Your brake system can be cleaned easily using a spray-on cleaner. Most brake cleaners require removing the tires and simply spraying the cleaner without disassembling any brake parts.
Warning:
- Take care to not spray the cleaner on your skin or eyes. Use protective wear while using the spray.
- Do not apply the brake cleaner on any car component that is hot, as it could easily oxidize the metal and release poisonous gases.
- The brake cleaner can damage your car's paint. So, properly cover the exposed areas before applying the cleaner.
How often should I change my brake fluid?
Replacing brake fluid is often an overlooked process of a car's maintenance routine. The brake fluid should be replaced once in two years or as specified in the owner's manual.
Can the brake drums and shoes be installed by a DIYer?
If the DIYer is good at handling replacement tasks that require a lot of labor, installing brake drums and shoes is feasible.
Note:
- Ensure that you follow the safety measures while replacing the brake drums and shoes.
- Refer to the owner's manual even for minor clarifications.
You can find installation tips and replacement procedure guides for various parts, and other related articles in this link: Repair Brake System


