Understanding Turbo Engine Layouts
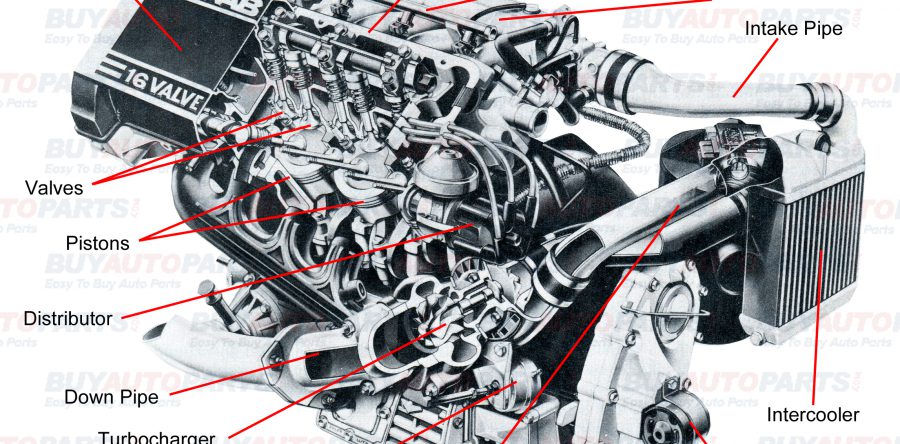
All internal combustion engines have the same basic components. These parts and accessories use dynamic cooperation to run the motor. While it is true that the rotary motor is different than other motors, keep in mind that all motors (including turbocharged motors) have similar attributes – in essence, they’re basically the same. This diagram shows the major components and pieces of your average turbocharged motor. For this illustration, the motor shows the basic engine parts and layout of a turbo Saab.
If you understand where the turbo sits and how the pistons interact with the valves, this information can help you diagnose engine performance issues. Armed with this knowledge, you’re better equipped to take on turbocharged motor DIY repair projects.
Buy Auto Parts is committed to helping you understand your car better. If you have a turbocharged motor, or are interested in understanding how turbo works, this diagram and basic engine parts is a great place to get started.
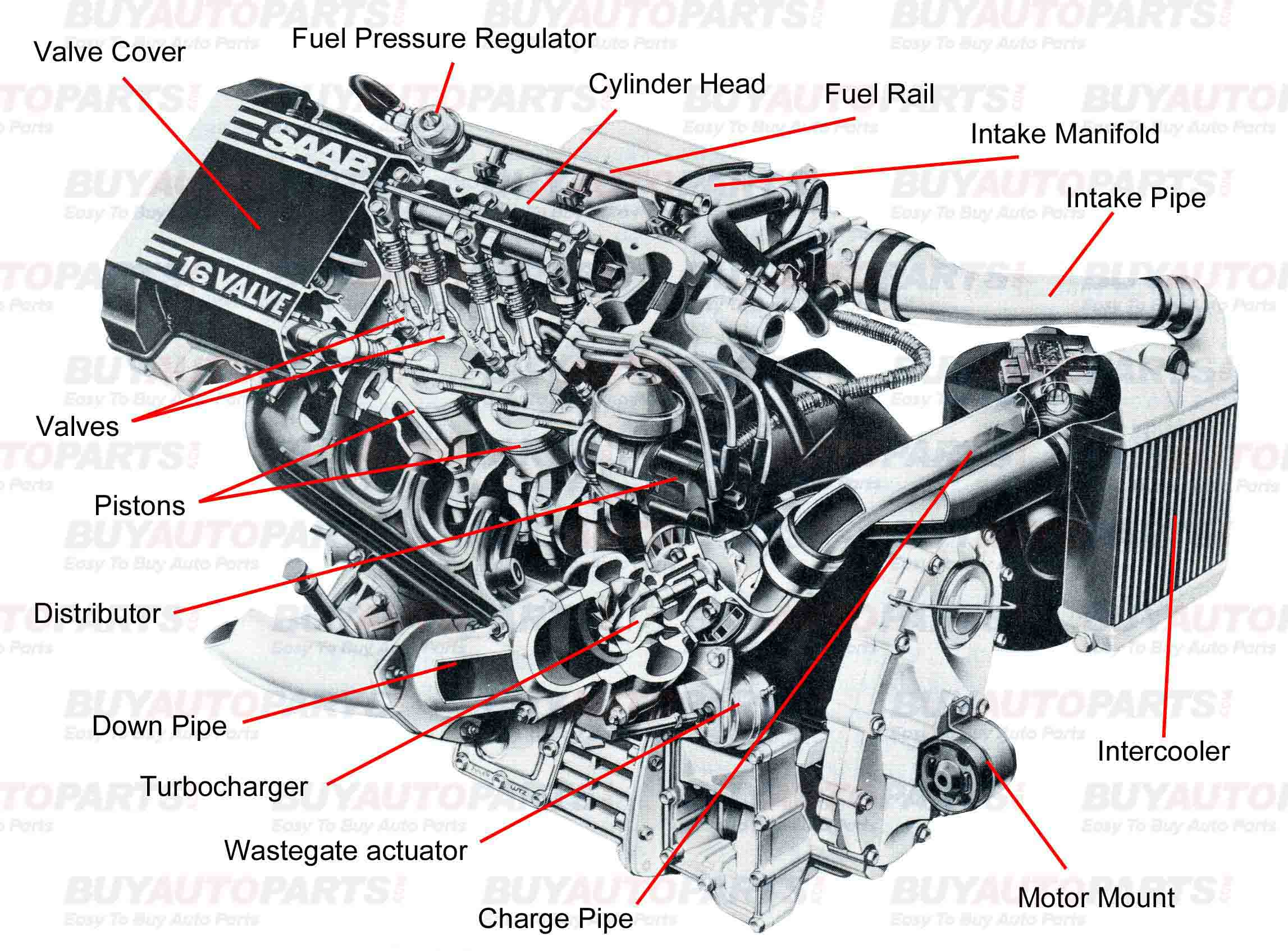
Basic Engine Part Descriptions
Valve Cover - This is the term used for the cover that is over the main valve body.
Fuel Pressure Regulator - Used to keep the fuel pressure constant even if it fluctuates from the fuel pump.
Cylinder Head - This is the unit that houses the valve body and other components at the top of the motor such as cam shafts and springs.
Fuel Rail - This unit carries the fuel to each individual fuel injector and also holds the injectors in place.
Intake Manifold - The air being pushed into the engine runs through this manifold and is dispersed evenly into the cylinders.
Intake Pipe - The intake pipe carries the charged air from the turbocharger into the intake manifold.
Intercooler - A device that allows the heat created by the turbocharging process to be dispersed before entering the intake of the motor.
Motor Mount - This unit attached the motor to the frame of the engine bay and has a bushing that allows for a small amount of play to keep the motor from rocking the car.
Charger Pipe - This is a pipe that carries the hot air from the turbocharger to the intercooler.
Wastegate Actuator - This unit controls the wastegate door with a pressure sensitive spring that will allow the wastegate to open once the pressure or boost reaches a certain point.
Turbocharger - This unit uses the exhaust gases to spin the shaft inside the unit which is attached to the impeller on the intake side. When the impeller speed reached a certain point it will begin to build boost inside the cylinders and this is referred to as spooling the turbo. This is an important concept for understanding how the turbo works.
Downpipe - Used to carry the spent exhaust gasses away from the motor and to the exhaust system of the car.
Distributor - This unit sends the correctly times spark to the plugs to ignite the fuel in the cylinders.
Pistons - These are the units that slide through the cylinder and cause compression. In the end of their upward stroke, the ignition of the fuel mixture forces the pistons back down and this process creates horsepower.
Valves - The valves open to allow the air to enter the cylinder and then close to allow for the ignition. Next they open to allow the spent gasses out of the cylinder and then close to begin the process again.