A critical component of today's modern vehicle is the sensor that measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. This sensor works with the vehicle's Electronic Control Unit (ECU) to constantly maintain the operational efficiency of the engine. If the oxygen content in the exhaust gas is too high (a lean mixture) or too low (a rich mixture), the sensor is able to transmit this information back to the ECU, which in turn adjusts the amount of fuel to be sent to the cylinder in order to maintain the perfect air to fuel ratio.
Not all vehicles have sensors with the same output characteristics and these sensors are not interchangeable. It is important to confirm the sensor type before making the repair.
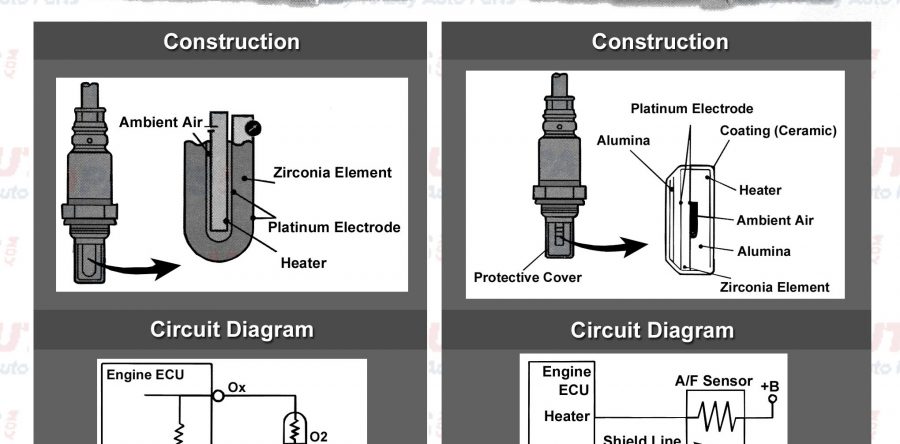
In vehicles equipped with a narrow-band oxygen sensor, the output voltage changes in accordance with the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. The ECU uses this output voltage to determine whether the present air/fuel ratio is richer or leaner than the stoichiometric air/fuel ratio (14.7:1).
Vehicles equipped with an air-fuel ratio sensor have approximately 0.4V constantly applied to the sensor, which outputs a current that varies in accordance with the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. The ECU converts the changes in the output current into voltage allowing a response that is directly proportional to the input of the present air/fuel ratio in the exhaust system.
Differences between an oxygen sensor and an air-fuel sensor:
The exterior appearance of the air-fuel ratio sensor and oxygen sensor may be very similar but that's where the similarity stops.
a) Using a light bulb analogy, the oxygen sensor sends voltage to the vehicle's ECU and acts like an on/off switch turning the bulb on and off. The air-fuel ratio sensor receives voltage from the vehicle's ECU and acts like a dimmer switch making the bulb brighten and dim.
b) A narrow-band oxygen sensor determines whether the engine is running rich or lean without measuring the extent of richness or leanness. A wide-band oxygen sensor or the air-fuel ratio sensor is efficient in determining how much rich or lean the engine is running at any given time. This makes the air-fuel ratio sensor preferable over oxygen sensors in modern automobiles.
Symptoms of a defective Oxygen/Air-Fuel Ratio Sensor:
Since both the sensors basically measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust, they exhibit similar symptoms when they go bad. Common indications of a bad oxygen/air-fuel ratio sensor include rough idling, engine pinging, poor gas mileage and increased exhaust emissions. One of the first symptoms of a faulty sensor is the lighting up of the "Check Engine" light.
Purchase Oxygen Sensors at Buy Auto Parts!
If you are looking to buy an oxygen sensor, Buy Auto Parts is the right place. We will get you the oxygen sensor once you select your automobile's right year, make and model. Coming with an industry-leading warranty at unbeatable prices, our oxygen sensors are meticulously tested to meet or exceed industry standards. We also offer free shipping for purchases over $99. Your order will reach you on time, as it will be shipped from one of our warehouses close to your location. If you have trouble in locating your part, our support team is at hand to help you: call us at or leave us an email at [email protected]. You can browse through our extensive line of throughly-tested OEM replacement and aftermarket parts for every make and model.