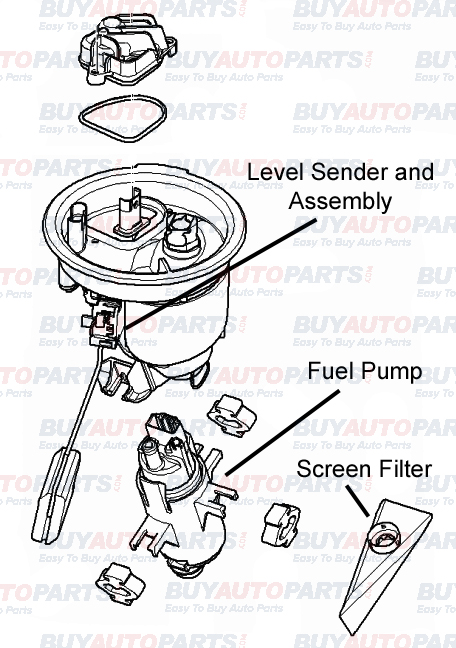
The fuel pump assembly in a vehicle is responsible for sending the required amount of fuel at the right pressure and time to the engine. The assembly consists of a few key parts such as the screen filter, fuel pump and fuel pressure regulator. Let us start at the bottom of the unit and work our way up.
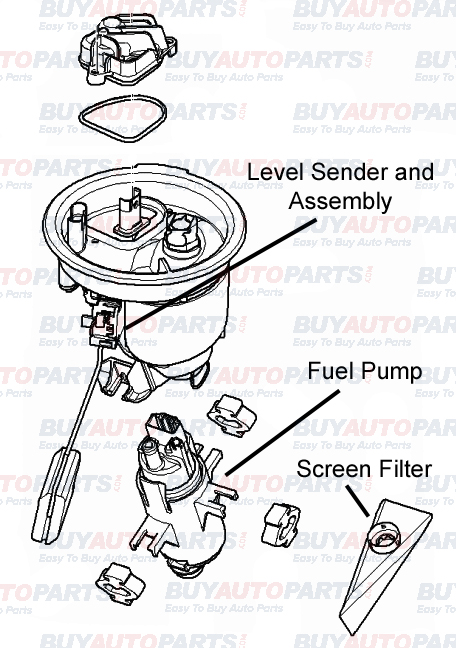
The filter screen is at the bottom and it is there to catch large debris that may be in the tank itself. The screen filter should not be confused with the fuel filter.
The fuel pump itself is the unit that pulls the fuel from the tank and pushes it into the fuel lines and eventually to the motor. Generally, the pumps are either of the pusher or puller type. Mechanical pumps, which are used in carbureted vehicles, fall under the pusher type while electric pumps employed in vehicles with fuel injection fall under the puller type. The pusher pumps are efficient in drawing the fuel from the fuel tank. On the other hand, puller pumps are comparably less efficient in extracting fuel from the tank. However, they are better than pusher pumps in delivering fuel to the engine. This is the reason why pusher pumps are mostly fitted in the fuel tank itself.
Mechanical pumps are driven by the engine's crankshaft while electric pumps are operated by means of the pump relay, which turns on when the ignition is switched on. Modern cars have electronic fuel injection systems that dictate to the fuel pump relay when to run and shut off the pump. Mechanical pumps generate a fuel pressure that varies from 4 to 8 psi. Electric fuel pumps generate a pressure that varies from 20 to 70 psi. In electric pump systems, the voltage transmitted to the fuel pump is monitored by a Fuel Pump Driver Module or FPDM.
The fuel pressure regulator, located on the fuel line, maintains the pressure of fuel sent to the engine. It is also responsible for pushing the excess fuel down the return line. There is a level sender unit that houses the float, which calculates the amount of fuel in the tank and sends the readings to the fuel gauge on the dash of the car. Finally, on the very top of the unit, there is a hose assembly which is where the fuel lines hook up to the assembly and direct the fuel to and from the engine.
While the fuel pump assembly is responsible for pushing the fuel at an optimal pressure, the fuel injection system comes into the picture when the pressurized fuel needs to be delivered to the engine. The fuel injector has a nozzle through which fuel is sprayed into the cylinder.
Problems with fuel system components will obviously affect the performance of the engine. Generally, when fuel system components go bad, it will not provide the fuel at the optimal level/pressure, thereby lowering the engine power. Fuel system components will cause the Check Engine Light in your dashboard to glow. Other common symptoms include vehicle stalling and decreased fuel economy.
To ensure a proper working of the fuel system, the level of fuel in the tank should be maintained properly. Generally, it is not recommended to drive your vehicle when the level of fuel in the gas tank is below a certain level. Doing so will damage the fuel system components and can result in an untimely failure.
Inspecting the fuel components on a regular basis is vital for a maintaining good performance of the fuel system.