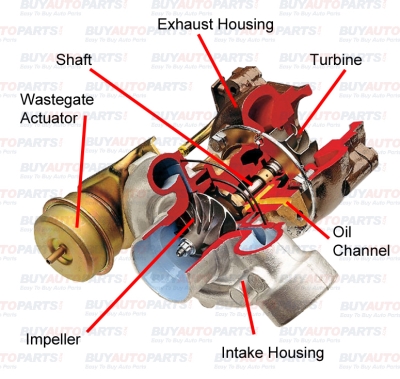
The diesel motor, in many ways, is just like a gasoline motor in form and function. The main difference is the way it causes combustion. A diesel engine uses the compression of the cylinder to ignite the air-fuel mixture during the combustion process. The correct amount of diesel fuel and air is important for the proper operation of the diesel motor. Turbochargers are included in a diesel engine system to increase the power generated by it. This page describes the construction, function of a turbocharger in a diesel system and its symptoms of failure.
The diesel turbo has two important sections: the turbine and compressor. The turbine housing is what draws the exhaust gases and rotates the turbine wheel. The turbine wheel is attached to the compressor wheel via a shaft. When the turbine wheel rotates, it causes the compressor wheel to spin. This action compresses the air and pushes it into the engine's combustion chamber. Compressed air can burn with a greater amount of fuel to provide more power. This is the basic mechanism behind the turbocharger. Most turbochargers also include an intercooler installed between them and the engine. This cools the compressed air from the turbocharger, before it is delivered to the engine. Compressed air when cooled becomes more denser and hence can burn a large amount of fuel than compressed air at the normal temperature. The increased power provided by the turbocharger is usually referred to as the “turbo boost”. You can check the boost gauge in your vehicle to know the amount of boost provided by your turbo. Turbos can range in size, efficiency, type and are usually known as power adders due to the fact that they push the engines horse power higher than it would be at the naturally aspirated level.
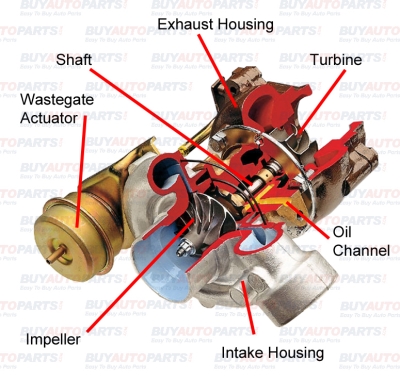
Generally, diesel engines cannot draw as much air as compared to gasoline engines. This is why diesel engines generate a lesser power at higher rpms than gasoline engines. Therefore, adding a turbo to a diesel engine can help lessen this problem considerably. In fact, turbochargers were originally intended to be used in diesel engines.
Since diesel oil burns at a lower temperature than gasoline, it generates higher volumes of exhaust gases. Therefore, a diesel turbo should be designed to handle a large amount of exhaust gases. This is why diesel turbos generally include a larger turbine and compressor sections.
The goal of a diesel turbo is to increase the air flow rather than increasing the combustion pressure, since diesel engines naturally operate under higher pressures. So, the boost provided by a diesel turbo is generally low, in the range between 5 and 8 psi.
By adding a diesel turbo to your car, you can improve your vehicle's output power and mileage. It is known that diesel engines emit a louder noise than gasoline engines. However, adding a turbo to the diesel engine can also reduce the noise significantly.
Your turbocharger can fail over time due to natural wear and age. The common symptoms of a damaged turbo include reduced engine power and increased emissions. A bad turbo will cause the Check Engine Light in your vehicle's dashboard to come on.
Buying Diesel Parts and More
Do you drive a vehicle with a diesel motor? If you do, chances are that you need more information on diesel engines or need to know how much a turbocharger would cost.
Visit our How To Section for more information on auto parts and general automotive knowledge.
If you are in the market for a diesel turbocharger for your vehicle, please visit this page: Turbochargers
You can also read our buyer's guide for more information on buying a turbocharger.